Arvind Lakshmikumar is trying to use Silicon Valley smarts with his venture, Tonbo Imaging, to give hidebound defence forces across the world some bite.
The Bengaluru-based provider of imaging and sensor systems has moulded itself as an asset-light provider of cuttingedge solutions, just like Apple in consumer electronics, Airbnb in hospitality and Uber in commuting.
Tonbo has tried to take a fresh approach to the stodgy defence market by building a business that relies on lowcost, consumer-grade electronic gear and contractors for manufacturing, focusing its energiesBSE -3.06 % on customers and building a bank of intellectual property. For the first four years of its existence, though, Tonbo had zero revenue, as the founders focused on building products.
In year one — 2013 — it netted just $1.5 million in revenues, which went up to $3 million 12 months later. By December 2016, the company, backed by Artiman Ventures — with a new tranche of $20-25 million in funding just weeks away — hit the jackpot. Tonbo announced it had bagged a $100 million deal to manufacture and export night vision sights to Peruvian army.
In an industry known for being an old boys’ club, reliant on an intricate and inefficient network of middlemen to get things done, a bunch of upstarts is hoping to unseat entrenched players. India’s defence market can be intimidating.
Contracts are notoriously slow to be awarded; getting a look-in involves knowing the right middleman; and, with no upfront payments, startups can find themselves struggling against the tide.
“Business cycles are long and often frustrating,” says Ankit Mehta, cofounder of ideaForge, a Mumbai-based provider of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV).
“But the payoff at the end is massive.” Other entrepreneurs agree. “The possibilities of innovation in this market are limitless,” says Praveen Bhaniramka, founder of VizExperts, a provider of geographic information systems. “The unique challenges of this market require one to look for solutions that span multiple technology domains.” The firm’s GeorbIS product, used by the National Security Guard (NSG) and Border Security Force (BSF), deploys a combination of geographic information system (GIS) , gaming and simulation to devise solutions for the needs of defence forces.
VizExperts’ solutions address the training and operation planning requirements of the Indian defence forces. The firm has built products in domains like 3D GIS, system modelling and simulation, multi-data fusion, 3D visualisation and virtual reality. The GeorbIS 3D GIS platform is a geospatial suite widely used by the Indian defence forces and law enforcement agencies for geospatial intelligence-driven decision support. The technology, for instance, helps with simulation-based training requirements of the forces.
Business is apparently booming: Bhaniramka claims revenues will top Rs 40 crore this year from around Rs 23 crore in 2015-16.
The big fight
ideaForge has been on a slow boil, notching up one customer at a time for a couple of years, before stepping on the gas recently. ideaForge’s first customer was the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the state-run R&D unit. Then, sales were sealed for state police forces, before deals with paramilitary and military units too were closed. Now, ideaForge’s gear is used to track everything from floods to militancy to anti-Naxal operations nationwide.
To make a mark in this market, these startups have had to pick fights with companies outside their weight class and have slowly begun to make a mark. Recently, the Indian Army’s Northern Command was on the hunt for night vision goggles, with a budget of Rs 23 lakh. Not only did Tonbo unseat the existing provider, a state-run company, but it offered a new-generation product for as little as Rs 14 lakh.
To build a low-cost product, the team at Tonbo has benefited from some key changes in the consumer electronics market over the past two decades. Traditionally, consumer electronics platforms were costly and inefficient, and companies looking to leverage them had to build their own custom solution.
However, as electronics has proliferated and become commoditised, it has become possible for firms such as Tonbo to use them cheaply and quickly. “Some 20% of the cost of every large system like a submarine or even a gun is the imaging sights,” says Lakshmikumar.
Leo Mavely, cofounder of Axio Biosolutions, a provider of hemostats that control bleeding, is also seeing strong traction for its products: “We have just begun to make inroads into the Indian market, with the forces quickly realising the value of a high-quality hemostat in the heat of battle.”
Axio Biosolutions, a company backed by Accel Partners and IDG Ventures, benefits because there are only four or five providers of hemostats to defence forces and their products are far costlier (a US import previously cost Rs 13,000-14,000 per pack compared with Rs 2,000 from Axio).
The supply of the hemostats was also sharply regulated. The shortage was acutely felt by the forces many times. Like in Chhattisgarh during a Naxal attack two years ago. The forces took two or three days to return from remote location to their bases. Treating wounds and stopping bleeding was a struggle with limited medical equipment at their disposal.
An evacuation was extremely risky since helicopters could get shot down. That was reason enough to bring Axio aboard. Over the past couple of years, Mavely and his team have made big progress, signing up with several army units, and paramilitary forces such as the BSF and the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP).
Others have found less bloody ways to target the market. Lakshmikumar aggressively targeted overseas buyers for its products — the first customer was US Special Forces Operations —before building a strong case for India’s defence mandarins. Now, he has big plans for the business and for annual revenues to touch $100 million in three or four years. “We want to build a global defence solutions provider from India,” he says.
Similar ambitions are echoed by Aakash Sinha, cofounder of Omnipresent Robotics, a developer of UAVs, drones and robots. “In a couple of years, every battalion of the army and paramilitary will have drone capabilities and that could open up a market of over 1,000 vehicles,” he says. Omnipresent already has a couple of dozen UAVs deployed and hopes to sell at least 35 to 40 of them annually.
Sinha has some pedigree in this field. He worked for nearly eight years with large US defence companies such as Lockheed Martin and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the US entity that focuses on emerging military technologies: Sinha claims to have been part of a team that built a driverless car for DARPA in a robotics challenge.
Awarded a DARPA Finalist Medal (a rare commendation, he claims, for a non-US citizen), he also worked as part of a team that developed iRobot Packbot, a series of military robots deployed by the US Army. Later, Sinha started Omnipresent in India, and his first project was building Angad to sense and defuse bombs. The project is under military trials with the DRDO.
In contrast, Parag Naik, cofounder of Saankhya Labs, an Intel Capital-backed developer of software-defined radio for defence forces, started off attempting to develop broadcast receivers, but discovered that the business model didn’t fly.
Instead, the company used some of its in-house skills to pivot to developing these radios, with 26 different chipsets squeezed into them, to let defence personnel communicate on everything from 2G networks to satellite telephony.
“The complexity of our technology is comparable to, if not ahead of, competitors from the US and Israel,” he says. “Our chipsets allow defence forces to use the same equipment, but with software upgrades, to keep pace with the latest communication technologies.”
While Saankhya began by working with the India Space Research Organisation (Isro), the national space agency, it is now focused on building a robust business in the defence sector. It has bid for a couple of contracts with t ..
While Saankhya began by working with the India Space Research Organisation (Isro), the national space agency, it is now focused on building a robust business in the defence sector. It has bid for a couple of contracts with the army and is eyeing deals with other military and paramilitary units. “While there is a massive potential in the Indian defence market, the mindset towards private players, especially startups, has to yet fully change,” says Naik.
Innovation nation
According to Sinha of Omnipresent, the robotics and UAV venture, some key technical breakthroughs in defence (tactical robots, stealth technology for planes and even the internet) were all seeded in startups backed by the US defence.
The US defence aids startups, with programmes such as Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR), which has founded some 5,000 startups since 1982 and given them early funding and the opportunity to flourish — or fail. “In India, there is no handhold and it is very difficult for startups to get in and make a mark,” says Sinha.
This may be slowly changing, with decision-makers warming up to these upstarts, as the forces push to modernise their gear. With state labs such as DRDO and government-owned firms unable to keep pace with technology shifts, the private sector may have a pivotal role to play.
Some innovative schemes may also be helping, says Naik of Saankhya. For instance, there is the “Make” category, where the government will refund R&D costs in 24 months if they don’t place a definitive order; an Army Research Bureau is also in the works to catalyse innovation; and an electronic development fund has reportedly identified 15-20 ventures to back. “Across defence forces, there is strong interest to not keep it business-as-usual,” adds Naik.
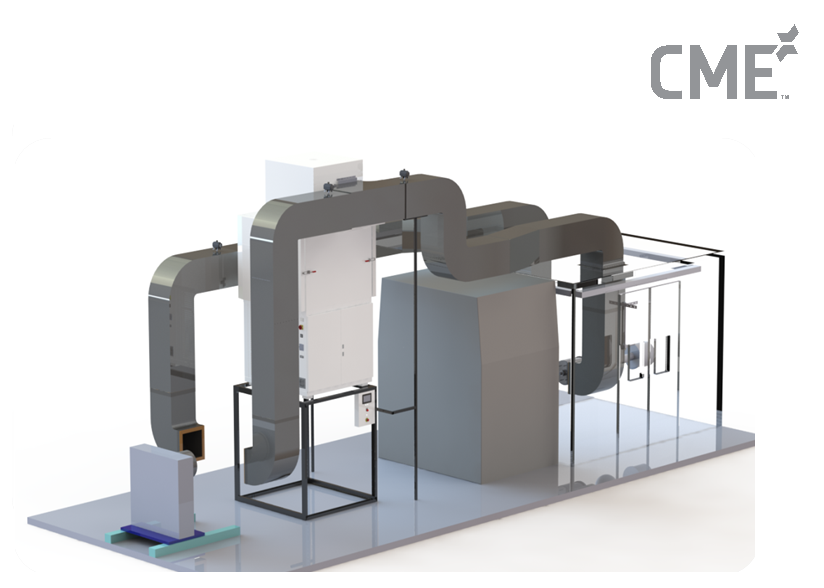
This shift couldn’t have come a moment too soon. “Opening up defence deals to private companies will revolutionise the outlook for this sector,” says Prajwal Crasta, founder and CEO of CM Envirosystems, a provider of environment-simulation testing technology.
The company’s equipment, for example, can mimic severe weather conditions, corrosion and altitude to test missiles, satellites and parts used in an assortment of military vehicles. While Crasta has to primarily deal with defence quality labs to hawk his products, he has also had to face the inefficiencies of other units like government ordnance factories which, he says, sit comfortably at the bottom of the pile.
Despite his dim view of government agencies, Crasta says defence procurement has improved reasonably in the last couple of years, with more private sector participation, and state-run units like DRDO having to compete on an equal footing for some contracts.
“Time is money in today’s market,” he adds. “We have never seen DRDO move like this in the past.” Other factors too help companies such as CM Envirosystems; the recent push to indigenisation is only helping.
While the market may be changing, startups themselves need to evolve to keep pace. “Several startups may think that they have a viable product,” says Mavely of Axio, the hemostat maker.
“However, once they finish early trials and the real orders come in, their limited manufacturing capacity catches them out.” To try to build a manufacturing pipeline, Axio has built a factory in Ahmedabad district, with a capacity of 50 lakh units, with barely 2.5 lakh of this currently being used.
For example, the market for hemostats in defence and civil forces alone is 2 crore units. While some startups have got some funding to fuel their expansion plans, not all investors may be keen to back companies targeting the defence market.
“Since the cost of failure is really high in this industry, one needs to invest significant time and effort to ensure development of a world-class product,” says Bhaniramka of the GIS solutions vendor VizExperts.
“This results in higher gestation periods, which typical investors shy away from.” Instead, he and other entrepreneurs argue, longer term investors may be more suited to this field. “This is where the government’s role in supporting innovative technology companies can be a game changer.”
While the opportunity in India’s defence industry may be massive, no one’s about to put all their eggs in one basket. For example, Axio Biosolutions only gets half of its business from the defence market, with civilian businesses accounting for the rest.
The firm is also expanding internationally, with operations in 12 countries and counting. Meanwhile, other startups are also looking beyond the defence market — ideaForge expects to have an annual revenue of $100-120 million in the next few years and is stepping up its commercial, automotive and internet of things initiatives. Cracking the Indian defence market is going to be a long slog.